Energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings: A Sustainable Approach
Energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings pave the way towards a greener future in construction. By exploring innovative materials and design considerations, this discussion sheds light on the importance of sustainability and cost-effectiveness in modern building projects.
As we delve deeper into the realm of energy-efficient exterior materials, we uncover a world where environmental impact and cutting-edge technologies converge to shape the buildings of tomorrow.
Energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings
Energy-efficient exterior materials play a crucial role in construction projects by contributing to sustainability and cost savings. These materials help reduce energy consumption, minimize environmental impact, and enhance the overall efficiency of buildings.
Examples of commonly used energy-efficient exterior materials:
- Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs): These materials provide excellent insulation and thermal resistance, reducing the need for additional heating or cooling.
- Low-E windows: These windows have a special coating that reflects heat back into the room, reducing energy loss and improving comfort.
- Solar panels: These panels harness solar energy to generate electricity, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and lowering utility costs.
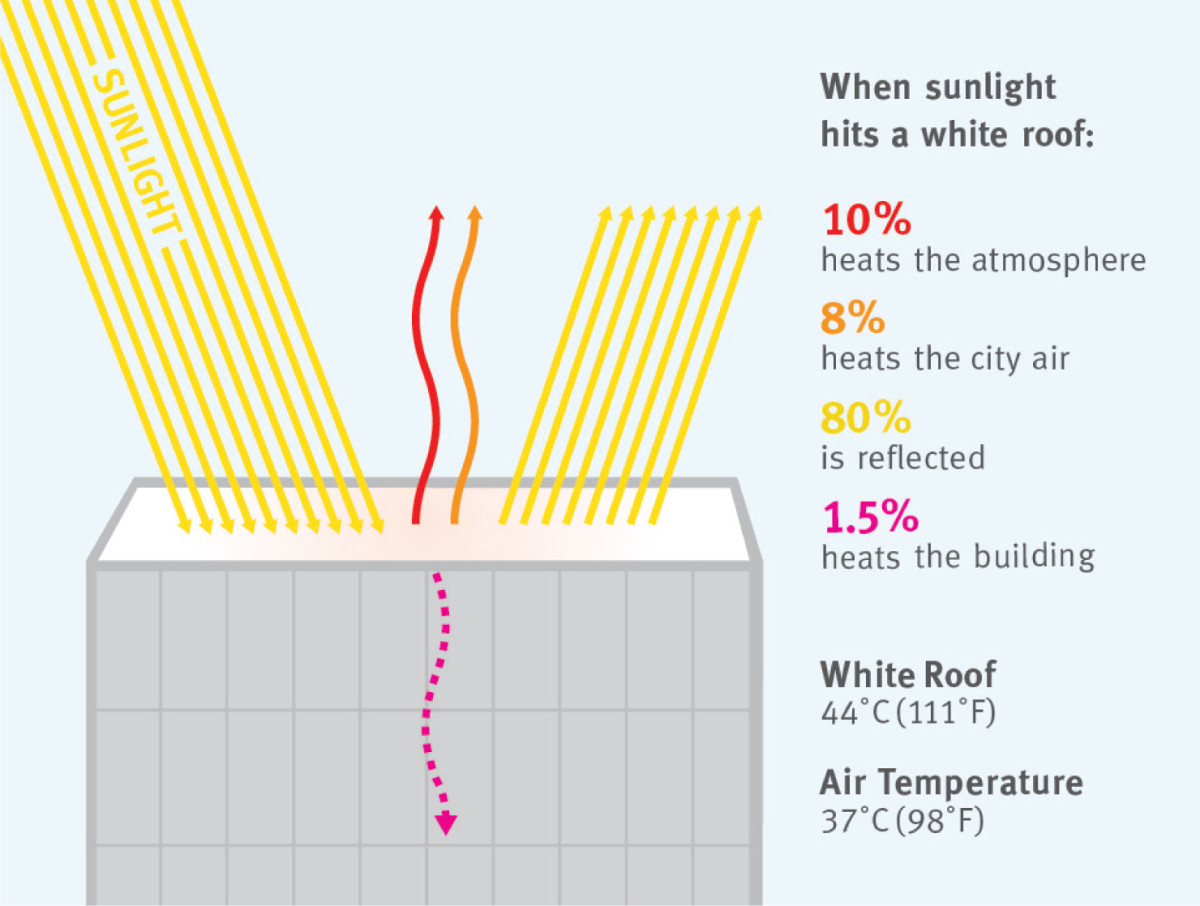
- Cool roofs: These roofs are designed to reflect sunlight and absorb less heat, keeping buildings cooler and reducing the need for air conditioning.
Benefits of incorporating energy-efficient exterior materials:
By using energy-efficient exterior materials, buildings can achieve sustainability goals and save on operational costs in the long run. These materials not only reduce energy consumption but also improve indoor comfort levels and air quality. Additionally, they contribute to a greener environment by lowering carbon emissions and promoting resource efficiency.
Types of energy-efficient exterior materials
When it comes to energy-efficient exterior materials for buildings, there are several options available, each with its own unique benefits and considerations.
Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs)
Insulated Concrete Forms are a popular choice for energy-efficient building exteriors. These forms consist of foam boards or blocks that are stacked to form the walls of a building, which are then filled with concrete. The foam provides excellent insulation, helping to reduce energy costs for heating and cooling.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)
Structural Insulated Panels are another energy-efficient option for building exteriors. These panels consist of an insulating foam core sandwiched between two structural facings, such as oriented strand board (OSB). SIPs are known for their high energy efficiency and quick installation process.
Insulated Metal Panels (IMPs)
Insulated Metal Panels are a newer material that combines the strength of metal with the insulation of foam. These panels are lightweight, durable, and offer excellent thermal performance. IMPs are a great alternative to traditional materials like brick and wood, providing superior energy efficiency.
Brick and Wood
While traditional materials like brick and wood have been used for centuries in construction, they are not as energy-efficient as newer materials like ICFs, SIPs, and IMPs. Brick and wood have lower insulation properties and can lead to higher energy costs over time.
Durability and Maintenance
When considering energy-efficient exterior materials, it's important to also evaluate the durability and maintenance requirements. While materials like ICFs and SIPs are known for their durability and low maintenance, IMPs may require more frequent inspections and maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Design considerations for energy-efficient building exteriors

When it comes to designing energy-efficient building exteriors, there are several key considerations to keep in mind. These include factors such as insulation values, thermal mass, and air tightness, all of which play a crucial role in the overall energy performance of a building.
Insulation Values
Insulation is a vital component of energy-efficient building design
Thermal Mass
Thermal mass refers to the ability of a material to store and release heat. Materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete, brick, or stone, can help regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing excess heat during the day and releasing it at night.
This can reduce the need for mechanical heating and cooling systems.
Air Tightness
Ensuring a building is air tight is essential for energy efficiency. Leaks in the building envelope can result in significant energy loss as conditioned air escapes and unconditioned air enters. Proper sealing of gaps and cracks, as well as the use of air barriers, can help improve the overall energy performance of a building.
Optimizing the Use of Energy-Efficient Materials
To maximize the benefits of energy-efficient materials in building envelope design, it is important to consider the orientation of the building, the local climate, and the specific energy goals of the project. Proper placement of windows, shading devices, and the use of passive solar design principles can further enhance the energy performance of a building.
Impact of Climate and Location
The climate and location of a building have a significant impact on the selection of energy-efficient exterior materials. For example, buildings in cold climates may require materials with higher insulation values, while buildings in hot climates may benefit from materials with high thermal mass to help regulate temperatures.
It is important to consider these factors when choosing materials for a specific project.
Environmental impact and sustainability

Energy-efficient exterior materials play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of buildings throughout their lifecycle. From production to disposal, these materials have the potential to minimize energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation. Let's delve into the various aspects related to the environmental impact and sustainability of energy-efficient exterior materials.
Analyze the environmental impact
During the production phase, energy-efficient exterior materials often require less energy and resources compared to traditional materials. This leads to reduced carbon emissions and resource depletion. Additionally, the use phase of these materials contributes to lower energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting, resulting in decreased operational carbon footprint.
When it comes to disposal, many energy-efficient materials are recyclable or reusable, further reducing waste sent to landfills.
Role of certifications like LEED
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification promotes sustainable building practices by recognizing projects that meet certain criteria for energy efficiency, environmental performance, and sustainability. By incentivizing the use of energy-efficient exterior materials, LEED encourages the construction industry to prioritize sustainability and reduce the environmental impact of buildings.
Innovative materials and technologies
Advancements in material science and technology have led to the development of innovative energy-efficient materials that push the boundaries of building design. From high-performance insulation to solar-responsive facades, these new materials and technologies offer improved energy efficiency, durability, and sustainability.
By incorporating these innovations into building projects, designers can create structures that are environmentally responsible and energy-efficient.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the use of energy-efficient exterior materials not only benefits the environment but also offers long-term savings and durability. By embracing these materials, we take a step towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly future in construction.
Key Questions Answered
What are some examples of energy-efficient exterior materials?
Common examples include insulated concrete forms, structural insulated panels, and insulated metal panels.
How do climate and location impact the selection of energy-efficient exterior materials?
Climate and location play a crucial role in determining the most suitable materials based on factors like insulation values and thermal mass.
What is the role of certifications like LEED in sustainable building practices?
Certifications like LEED promote sustainable building practices by recognizing projects that prioritize energy-efficient materials and design.